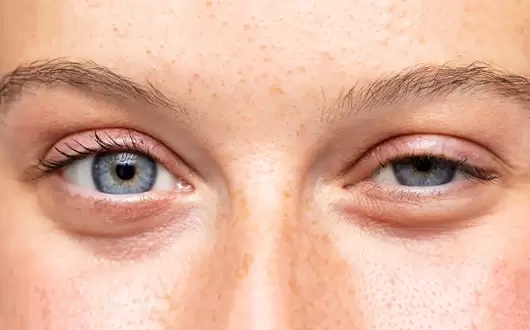
What is Ptosis? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Ptosis is an eye condition characterized by the drooping of the eyelid. This condition occurs when the upper eyelid is positioned lower than its normal place, which can restrict the visual field. Ptosis can affect one or both eyes and can happen at any age. In this article, you will find detailed information about the causes, symptoms, and modern treatment methods of ptosis.
What is Ptosis?
Ptosis refers to the drooping of the upper eyelid due to weakened eyelid muscles or nerve problems. This condition can impact visual ability, aesthetic appearance, and overall eye health. Ptosis can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (developed later in life).
- Congenital Ptosis: This type of ptosis is present from birth and is usually related to the improper development of the muscle responsible for lifting the eyelid.
- Acquired Ptosis: This type of ptosis can develop at any stage of life. The primary causes include aging, eye surgeries, trauma, nerve, or muscle problems.

Causes of Ptosis
Several factors can contribute to the development of ptosis. The main causes are:
- Aging: During the aging process, the eyelid muscles may weaken and stretch, leading to ptosis. Age-related ptosis usually develops more slowly.
- Trauma and Injuries: Injuries to the eye can damage the muscles or nerves of the eyelid, causing ptosis.
- Nerve Problems: Damage to nerves or nerve diseases (such as myasthenia gravis, Horner's syndrome) can weaken the eyelid muscles and cause ptosis.
- Muscle Diseases: Muscle diseases affecting the eyelid muscles (such as muscular dystrophies) can lead to ptosis.
- Eye Surgery: Ptosis can occur due to damage to the eyelid muscles or nerves during cataract or other eye surgeries.
- Congenital Anomalies: Some children are born with ptosis due to the improper development of the muscle that lifts the eyelid.
Symptoms of Ptosis
The symptoms of ptosis vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. The most common symptoms are:
- Drooping or lower positioning of the upper eyelid
- Narrowing or restriction of the visual field
- Fatigue and discomfort around the eyes
- Attempts to open the visual field by raising the head or eyebrows
- Frequent blinking or squinting

Diagnosis of Ptosis
The diagnosis of ptosis is made through examinations and tests performed by an ophthalmologist. The diagnostic process generally includes the following steps:
- Physical Examination: The doctor checks the condition, mobility, and function of the eyelid muscles.
- Vision Tests: Various vision tests are conducted to measure visual field restriction or visual ability.
- Nerve and Muscle Tests: Additional tests may be required to determine if nerve and muscle diseases are causing ptosis.
- Specialized Examination: In some cases, specialized examinations or radiological tests (MRI, CT) may be required to investigate underlying causes of eyelid drooping.
Modern Treatment Methods for Ptosis
The treatment of ptosis varies depending on the cause, type, and severity of the condition. The most commonly used treatment methods are:
- Ptosis Surgery: One of the most effective methods for treating ptosis is surgical intervention. During ptosis surgery, the doctor strengthens or shortens the muscles that lift the eyelid. This surgical method is more commonly applied in congenital or severe ptosis cases.
- Nerve and Muscle Treatment: If ptosis is associated with nerve or muscle diseases, treatment should be carried out alongside the treatment of these diseases. This can be done through medications, physiotherapy, and other special procedures.
- Botox Injections: Botox injections may also be used in the treatment of ptosis. Botox helps restore the function of the eyelid muscles and can provide temporary relief in certain cases.
- Glasses and Lenses: In some cases, special glasses or lenses may help temporarily manage ptosis.
- Regular Eye Examinations: Regular eye examinations are essential to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and check for the progression of ptosis.
Tips to Prevent Ptosis
Although it is not always possible to prevent ptosis, some measures can help protect eye health:
- Regular Eye Check-ups: Regular eye examinations with an ophthalmologist are essential to maintain eye health.
- Eye Protection: Use protective eyewear to prevent eye injuries, especially during risky activities.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding stress can improve eye and overall health.
- Management of Muscle and Nerve Problems: Timely diagnosis and treatment of nerve and muscle diseases can reduce the risk of ptosis.
Conclusion
Ptosis is a serious eye condition characterized by drooping of the eyelid, which can affect visual ability. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent vision loss and other complications. Regular eye examinations and consultations with a doctor are important to reduce the effects of ptosis and support the treatment process.
This article is for informational purposes only. It is not intended for clinical or therapeutic purposes. For this, you can make an appointment with a professional doctor (Dr. Günel Xalıgverdiyeva).