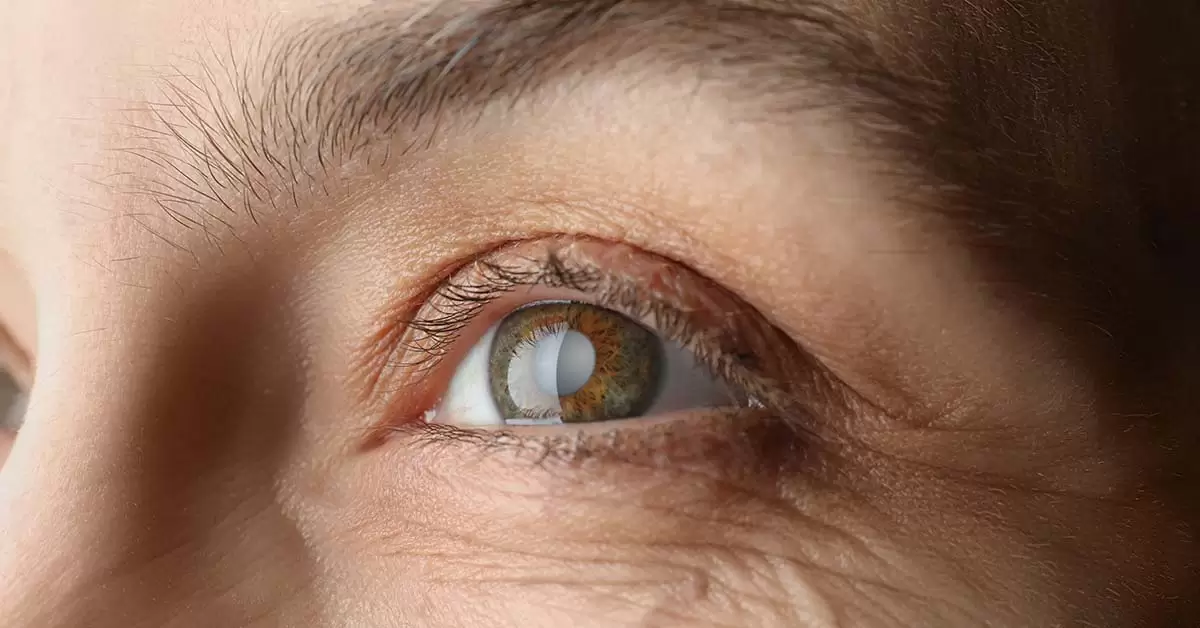
Cataract is characterized by the clouding of the normally clear lens of the eye. This condition, commonly referred to as "clouded lens," usually occurs in individuals aged 60 and older due to age-related factors. This is because the human eye is one of the sensory organs most affected by the aging process. However, the disease is not only observed in elderly individuals, as congenital, genetic, and environmental factors can also contribute to the development of certain types of cataracts.
Cataract is a common eye disease in older adults. Our eyes have a clear lens that refracts incoming light. Over the years, this lens loses its transparency and becomes darker, foggier, and cloudier. This leads to less light reaching the retina, and gradually, our vision diminishes. Colors lose their vibrancy. Since cataract progresses slowly, many people may not realize that their vision is deteriorating. After some time, the decrease in vision can lead to difficulties in activities such as driving at night, reading newspapers, and similar tasks. Many people try to solve this problem by increasing the amount of light in their homes or using glasses, but the real solution is surgery.
The causes of cataracts are quite varied. The components that make up the eye lens are primarily water and proteins. When these proteins become damaged over time and due to various factors, they can form permanent protein particles in the lens, leading to cloudiness. The common causes of cataracts can be listed as follows:
In the early stages, cataracts may present as slightly blurred vision, faded colors, and particularly difficulty seeing at night. The common symptoms include:
Many types of cataracts progress slowly. One of the early symptoms, blurred vision, may not cause significant discomfort. However, if the disease is not treated, it progresses, and vision becomes completely cloudy. The patient is unable to perform daily tasks.
Failing to start treatment in time can also lead to other diseases like glaucoma. Such cases increase the risk of permanent vision loss.
The congenital form of the disease can appear in newborns. Additionally, the disease may develop during childhood for various reasons. The symptoms of cataracts in infants and children include:
The answer to this question varies from person to person and depends on the type and severity of the cataract.
In the early stages of cataract development, the eye experiences slightly blurred or foggy vision. This situation can be described as looking through frosted glass. Over time, this blurred vision increases, and detailed vision becomes impossible.
People with cataracts see the world as blurry, faded, and in pastel tones, as if looking through frosted glass.
Cataract is diagnosed through an eye examination conducted by an ophthalmologist. During the examination, it is confirmed whether the patient has any other eye problems. The criteria examined for the diagnosis of the disease are as follows:
The tests applied within this framework include:
Visual Acuity Test: The visual acuity test measures the patient’s ability to see fine details. The patient is asked to read images and letters arranged from large to small at both close and distant ranges.
Biomicroscopic Examination: With a biomicroscopic examination, other elements in the front segment of the eye are examined.
Tonometry: The lens with cataracts usually increases eye pressure. Therefore, the patient’s eye pressure is measured with tonometry.
Fundus Examination: This examination measures the effects of the disease on the retina.
Cataract treatment is only surgical. There is no medication treatment for it.
Cataract surgery involves the removal of the patient’s natural intraocular lens using various surgical techniques and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens. It is a microsurgical operation.
The surgery begins with numbing the eye using drops. A micro-incision is made at the corner of the eye, the cataractous part is removed using various surgical techniques, and finally, an artificial lens is placed through another incision, completing the surgery.
The most commonly preferred types of surgery include:
Phacoemulsification: This procedure involves the removal of the cataractous lens using ultrasound energy and replacing it with a lens through a small incision.
Laser Cataract Surgery: Cataract surgery - Femtolasik (FemtoSecond Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) is one of the most advanced laser surgical methods for correcting vision defects. In femtolasik surgery, a thin flap is created on the cornea using a femtosecond laser, and then the cornea is reshaped using an excimer laser. This method corrects vision defects, providing clear and precise vision. Femtolasik surgery stands out for its high precision and fast recovery time.
After cataract surgery, vision quality significantly improves. However, in some cases, the use of glasses or contact lenses may still be necessary.
If cataracts are present in both eyes, surgery is usually performed one week apart. This allows sufficient time for the treated eye to heal. In rare cases, a second cataract surgery may be required. The implanted artificial lens may lose its transparency and become cloudy over months or years. In such cases, laser surface cleaning can be performed to remove the cloudiness on the lens surface.
Cataracts can significantly reduce vision quality and lead to permanent eye problems. While age is a significant risk factor for cataracts, the disease can also be observed in younger individuals. As the vision problems caused by cataracts make life very difficult, specialists recommend surgery. Cataract surgeries ensure the recovery of approximately 90% of patients, and the procedures are effective, safe, fast, and relatively painless.
2024-07-17
2024-02-14
2024-02-14
2024-06-12
2024-06-13
2024-06-13
2024-06-13
2024-06-14
2024-06-14
2024-06-14
2024-06-14
2024-06-14
2024-06-14
2024-06-14
2024-07-31
2024-07-31
2024-07-31
2024-07-31
2024-08-12
2024-08-28
2024-09-05
2024-09-06
2024-09-14
2024-09-19
2024-09-19
2024-10-01
2024-10-02
2024-10-07
2024-10-21
2024-10-23
2024-10-29
2024-11-12
2024-11-18
2024-11-21
2024-11-26
2024-11-28
2024-12-03
2024-12-06
2024-12-10